Sexually Transmitted Diseases
Sexually transmitted diseases (also called STDs or STIs -- sexually transmitted infections) are infections that can be transferred from one person to another through sexual contact. According to the Centers for Disease Control there are over 15 million cases of sexually transmitted disease cases reported annually. Adolescents and young adults (15-24) are the age groups at the greatest risk for acquiring an STD, 3 million becoming infected each year.
It is important to recognize that sexual contact includes more than just intercourse. Sexual contact includes kissing, oral-genital contact, and the use of sexual "toys," such as vibrators. There really is no such thing as "safe" sex. The only truly safe sex is abstinence. Sex in the context of a monogamous relationship where neither party is infected with a STD is also considered "safe". Most people think that kissing is a safe activity. Unfortunately, syphilis, herpes, and other diseases can be contracted through this apparently harmless act. All other forms of sexual contact also carry some risk. Condoms are commonly thought to protect against STDs. Condoms are useful in helping to prevent certain diseases, such as HIV and gonorrhea. However, they are less effective protecting against herpes, trichomoniasis, and chlamydia. Condoms provide little protection against HPV, the cause of genital warts.
If you think you may have an STD or a related condition, see a doctor right away.
Why would I want to be tested for any sexually transmitted infections (STI)?
There are many different STIs. Some, like HIV, can cause serious illness and even death. Some, like Chlamydia and gonorrhoea, can cause infertility (not being able to get pregnant). The risk of developing serious health problems due to STIs can be reduced if the infection is diagnosed early, and best of all before there are any symptoms. If you have had unprotected sex (sex without using a condom), there is a risk that you could have an STI. Getting tested cuts your risk of ill health.
I have no symptoms. Does this mean I don't have a sexually transmitted infection (STI)?
No. Most people with an STI show no symptoms. If you have had sex without a condom, there is a risk that you could have an STI even if you have no symptoms and that means you could pass it on to future partners.
How is HIV passed on through sex?
HIV is present in blood, sexual fluids like vaginal fluids (in women) and in semen (in men). During sex, HIV can pass from the sexual fluids of one person to the bloodstream of the other, particularly where the lining of the skin or membrane is thin such as the vagina, urethra (tube that carries semen to the head of the penis) or anus (anal sex).
Can you get STIs from oral sex?
Yes. The commonest infection to be passed from the mouth is herpes - someone who has had cold sores can give genital herpes through oral sex. Infections such as gonorrhoea can be passed to the throat during oral sex. There is a very, very small risk that HIV could be passed through oral sex if somebody swallowed semen infected with HIV.
How can you tell if you have HIV?
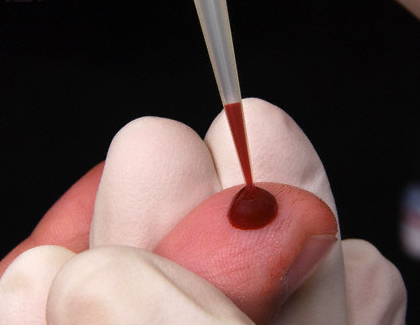
The only absolutely accurate way is to have an HIV test done on a blood sample. Many people are infected with the virus and not know it themselves, as they show no symptoms. When symptoms do develop, they can be very similar to symptoms caused by other illnesses. A blood test therefore is the only way to detect the presence of HIV
Common STDs
A partial listing of sexually transmitted diseases:
Chlamydia - Chlamydia is a very dangerous STD as it usually has no symptoms; 75% of infected women and 25% of infected men have no symptoms at all.
Gonorrhea - Gonorrhea is one of the most frequently reported STD. 40% of it's victims contract PID if not treated, and it can cause sterility.
Hepatitis B - A vaccine exists, but there's no cure; can cause cancer of the liver.
Herpes - Painful and episodic; can be treated but there's no cure.
HIV/AIDS - First recognized in 1984, AIDS is the sixth leading cause of death among young men and women. The virus is fatal involving a long, painful death.
Human Papalloma Virus (HPV) & Genital Warts - The most common STD, 33% of all women have this virus, which can cause cervical or penile cancer and genital pain.
Syphilis - Untreated, can lead to serious damage of the brain or heart.
Trichomoniasis - Can cause foamy vaginal discharge or no symptoms at all. Can cause premature birth in pregnant women.
Chlamydia
Type of Infection: Bacterial; from the chlamydia trachomatis strain which lives in vaginal fluid and semen
Mode of Transmission: Mainly through vaginal and anal sex; although it is much less common, it can also be passed on via oral sex and hand to eye contact
Symptoms: Chlamydia is known as the "silent" disease since up to 75% of women and 50% of men infected with it display no symptoms. When there are any chlamydia signs and symptoms, it is most likely abnormal vaginal or penile discharge (mucus or pus) and painful urination. Symptoms of chlamydia in women can also include abdominal pain, low-grade fever, pain during intercourse and the need to urinate more often. Chlamydia in men can also make itself known through inflammation of the rectum and swelling or pain in the testicles.
Treatment: Antibiotics are used to cure the infection. To ensure proper treatment, make sure you finish all your medication and refrain from having sex until your have finished treatment and tests have shown the infection to be gone. It is important to be treated as soon as possible. While the infection can be cleared up, any damage it may have done prior to treatment cannot be undone.
Gonorrhea
Type of Infection: Bacterial; from the Neisseria gonorrheae bacteria
Mode of Transmission: Mainly through vaginal, anal and oral sex. Bacteria are transmitted through vaginal and seminal fluids. Infection can show up in the genital tract, mouth or rectum.
Symptoms: Once infected, symptoms of gonorrhea can take between two and ten days to show up. In women, the cervix is usually the first site of infection. From there, the infection moves up into the uterus and into the fallopian tubes. Women are much more likely than men to be asymptomatic. If they do develop symptoms, they are likely to include: bleeding after sex, pain or burning sensation when urinating, need to urinate more frequently, vaginal discharge that is yellow or bloody, cramps, bleeding between periods, nausea or vomiting and fever. In men, gonorrhea symptoms include a puss discharge from the penis (white, yellow or green in color) accompanied by pain, burning sensation when urinating and swollen testicles. If the infection is in the rectum, symptoms will include discharge, anal itching and painful bowel movements. It is also likely that your feces will have blood in them.
Treatment: Gonorrhea treatment usually consists of a single dose of medication. Depending on your age and whether or not you are pregnant, some antibiotics may not be suitable to take. Because it is very common for people to be infected with both gonorrhea and chlamydia at the same time, gonorrhea treatments often include medication for chlamydia as well. While the treatment can clear up the infection, it cannot undo any damage gonorrhea may have done to your reproductive system prior to treatment.
Genital Herpes (HSV-2)
There are two types of herpes virus: Herpes Simplex Virus 1 (HSV-1) and Herpes Simplex Virus 2 (HSV-2). Generally, HSV-1 is associated with oral herpes, marked by the presence of cold sores around the mouth, while HSV-2 is thought to be the cause of genital herpes. However, HSV-1 has also been shown to cause genital herpes. The herpes virus lives in certain nerve cells in your body where it remains for life.
Type of Infection: Viral
Mode of Transmission: Through direct skin-to-skin contact with the infected area during vaginal, anal or oral sex.
Symptoms: Although first episode symptoms of genital herpes tend to be worse than subsequent herpes outbreaks, often a person’s herpes symptoms are so mild they go unnoticed. If you have been exposed to the virus, genital herpes symptoms can take between two and ten days to appear. Symptoms of herpes can include an itching or burning sensation and pain around the infected area. Painful lesions in the vagina, on the penis, around the genital area or anus, and on the thighs or buttocks often occur as well. Female herpes symptoms may also include vaginal discharge. Women frequently develop vaginal herpes, with herpes bumps and sores occurring in the vagina.
Treatment: Currently, there is no herpes cure. However, you can receive herpes treatment to help relieve your discomfort during an outbreak as well as reduce the frequency of outbreaks. There are three different types of herpes medication available, one of which may help lower the risk of herpes transmission.
HIV/AIDS
Type of Infection: Viral
Mode of Transmission: Mainly through unprotected vaginal or anal sex as well as through breast milk and sharing drug needles with an infected person. May also be infected by performing oral sex on some who is infected or by sharing sex toys that have not been cleaned. While there was once concern about the possibility of infection through blood transfusions, strict screening procedures have been in place in North America and Europe for many years to prevent an infection from occurring this way. People living in other countries, though, may still be at risk of infection through blood transmission.
Symptoms: The initial symptoms of HIV are similar to the flu and include fever, swollen lymph glands, headaches, muscle aches, fatigue and fever. However, many people fail to notice any HIV symptoms. Although the virus can remain dormant in your system for many years, the virus will continue to weaken your immune system by attacking your CD4 cells. Once the viral load overwhelms your CD4 cells (or T4 cells), you will likely develop an opportunistic infection resulting in a diagnosis of AIDS (Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome).
Treatment: There is no cure for HIV or AIDS. HIV medications usually include antiviral drugs that are taken to hinder the growth and even kill off part of the HIV cells. Although this HIV/AIDS treatment does not work for everyone, they can help to keep you healthy and avoid the progression of the infection to AIDS.
Complications: The main complications associated with HIV are the increased risk of serious illness, developing AIDS, and dying of an AIDS-related complication.
Consequences in Infants: Approximately 25% of all babies born to women with HIV will also be infected and will develop HIV symptoms within their first year of life. However, the use of antiviral drugs during pregnancy can significantly reduce your risk of transmitting the virus to your baby.
Crabs
Pubic lice are parasitic insects that typically infest the hair surrounding the genital areas. They can attach to coarse body hair on the arms, legs, armpits, eyebrows, and eyelashes. Also referred to as "crabs" because of their pincers, these lice can cause itchiness and irritation in those infected. Genital crabs are one of the most common sexually transmitted infections with more than 3 million cases occurring in the United States every year. Genital crabs can be treated with prescription lotions or shampoos as well as over-the-counter remedies.
Type of Infection: Parasite
Modes of Transmission: Pubic crabs are easily transmitted between sexual partners. Any close contact with an infected person can result in you contracting the parasite. If your sexual partner is infested with pubic crabs, you have a 95% chance of becoming infected yourself. Pubic lice can also be transmitted within families as the lice can live for short periods of time on bedding, towels, and clothing. However, this type of transmission is unlikely, as crabs can only live for 48 hours without human blood. Genital crabs are common in cramped quarters and can run rampant in hostels, military bases, and anywhere where large numbers of people are in close contact with one another.
Symptoms: Crabs symptoms include itching and irritation in the genital area. Since crabs live off of your blood, you may find bluish spots where the crabs have been feeding. Dark spots may also be visible on your skin or underwear. These spots are the crab feces and indicate a definite infestation. Additionally, you may be able to see genital crabs crawling around in your pubic hair or find nits (eggs) close to the bottom of the pubic hair shaft. It is also common to experience a slight fever and feel irritated and run down when you have a pubic lice infestation.
Treatment: Genital crabs are easily treated through prescription or over-the-counter shampoos. In order to combat the infestation, follow the directions on the shampoo carefully. It is important to clean any clothes, bedding, and linens that have may have been infested. Any items that can’t be washed should be dry cleaned or stored in a plastic bag for a few days. This will kill any pubic crabs that may be present. To treat pubic crabs that have infested the eyebrows or eyelids, use a specially prescribed lotion that is safe for the eyes.
Hepatitis B (HBV)
Hepatitis B is a potentially serious disease that attacks your liver. It is a viral infection similar to Hepatitis A and Hepatitis C. Unlike Hepatitis A, however, the Hepatitis B virus (HBV) has the potential to seriously damage your liver and can cause chronic illness and even death. About 1.25 million Americans are currently infected with Hepatitis B. 10% of those infected will develop chronic Hepatitis B, in which the virus can stay in the body for years. 15 to 25% of those infected with chronic Hepatitis B will die from liver disease. A Hepatitis B vaccine is now available to safeguard against this virus.
Type of Infection: Viral
Mode of Transmission: Person to person exchange of bodily fluids: unprotected vaginal, oral, and anal sex; infected pregnant mom to unborn child; sharing of contaminated drug needles; piercing the skin with contaminated tattoo or piercing needles; piercing the skin with contaminated medical or dental instruments; receiving contaminated blood or blood products; and receiving contaminated tissues or organs.
Symptoms: A large percentage of those infected with Hepatitis are unaware that they are infected. About 30% of those with Hepatitis B experience no symptoms. Others feel like they have just caught a common flu. Hepatitis B symptoms can include: yellowing of the skin or the whites of the eyes (jaundice); fatigue or extreme fatigue; loss of appetite; nausea and vomiting; abdominal pain; fever and chills; dark, tea-colored urine; and grey or clay-colored bowel movements. It typically takes 9 to 21 weeks from the time of transmission for symptoms of Hepatitis B to manifest. Hepatitis B signs and symptoms are more likely to occur in infected adults than in infected children. 1% of those infected with HBV will experience extreme side effects. This is known as fulminant hepatitis. Fulminant hepatitis requires immediate medical attention.
Treatment: There is no known cure for Hepatitis B. Most infections will clear up within a few months. Those chronically-infected can be treated using the following drugs: Interferon Alfa or Lamivudine. These drugs will not cure Hepatitis B but they can markedly slow down its development as well as decrease the chance of liver disease.
Syphilis
Syphilis is a sexually transmitted disease caused by the bacteria Treponoma pallidum. It is often called the "Great Imitator" because syphilis symptoms resemble those of other common diseases. It has also been given the names "Miss. Siff" and "The Pox". Almost 36 000 cases of syphilis are reported in the United States each year but many more go unreported. The majority of syphilis sufferers are male, accounting for about 60% of all cases. If caught early on, syphilis can be easily treated. However, if left untreated, syphilis can cause heart problems, psychological disorders, blindness, and death. Syphilis also increases the risk of contracting HIV, the virus that causes AIDS, by up to five fold.
Type of Infection: Bacterial
Modes of Transmission: Syphilis is almost always transmitted through sexual contact with an infected person. The syphilis bacteria can easily spread from the ulcers on an infected person to the mucous linings of the mouth, genitals, and anus of an uninfected sexual partner. Though unlikely, it is possible to contract the infection by coming into contact with the broken skin of an infected person. Syphilis can also be passed from an infected mother to her unborn child.
Symptoms: Syphilis symptoms occur in stages. Primary syphilis results in painless sores called "chancres." These usually appear on the genitals, but they can also appear on the lips, tongue, and other body parts. These chancres generally disappear within a few weeks, but if left untreated, the disease can progress to chronic stages. Secondary syphilis begins with the syphilis rash. This is an infectious brown skin rash that typically occurs on the bottom of the feet and the palms of the hand. Fever, sore throat, swollen glands, and hair loss can also be experienced. The third stage of syphilis can last for many years, and you may suffer from joint and bone damage, increasing blindness, numbness in the extremities, or difficulty in coordinating movements.
Treatment: If caught early, syphilis is easily treatable. A single dose of an intramuscular penicillin injection can cure those infected within a year. 24 hours after this injection, you are no longer infectious. Some people don’t respond to these penicillin injections, or cannot receive them due to allergies. Other antibiotics are used in these cases. Frequent blood tests over a two year period are required to ensure that the syphilis bacteria has left your system. Treatment will not reverse any damage suffered as a result of the syphilis infection